International Organization for standardization (ISO) is an independent, non-governmental, international organization that develops standards to ensure the quality, safety, and efficiency of products, services, and systems. The purpose of the ISO standard is to design to make products and services better and to make companies, governments and other organizations more efficient. Some of ISO standards are designed for specific industries, like the food industry, or design to help improve the environment.
ISO 178 Test Standard
Description For ISO 178
ISO 178 is an international test standard describes a method for determine the flexural properties of plastics. This test measures the flexural stress, strain, and modulus of rigid and semi-rigid plastics. The test uses a universal testing machine and a three point bend fixture to bend plastic test bars to acquire the data needed to make the calculations.
Two methods are outlined in the standard: method A uses a strain rate of 1%/min, method B uses two different strain rates: 1%/min for determination of the flexural modulus and %5/min or 50%/min, depending on the ductility of material, for the determination of the remainder of the flexural stress-strain graph.
Specimen For ISO 178
Round, square, rectangular or polygonal cross-section test pieces shall be used in the test.

Jigs For ISO 178
The following are the equipment used in this test:
1. Bending device with two supports and a former
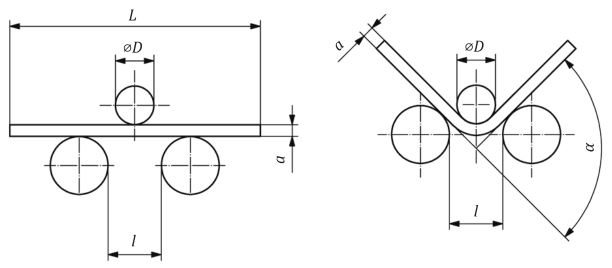
The 3-point bending jig was mounted on an electromechanical material testing machine. The 3-point bending jig is an easy-to-use fixture that relies on the test machine to maintain alignment between the top and bottom parts.
2. Bending device with a V-block and a former
Extensometers
This test does not require an extensometer because the purpose of this test is not to measure the displacement of elongation.
Type of UTM Machine
1. VEW 2308

The machine is designed by mechanical-electrical integration, the composition of the force-measuring Sensor, transmitter, microprocessor, mechanism of load drive, computer and color inkjet printer. The high-precision electronic motor can be set to five-speed, the components are connected by plug-way, Floor-standing models, it is taken account of modern industrial design and ergonomics in modelling and Coating.
It can be tested with all the materials in the stretch, compression, bending, shear, embedded relay, Peeling. tearing, crack, etc, such as rubber, plastics, leather, metal, nylon wire, fabric, paper, aerospace, packaging, construction, petrochemical, electrical, vehicle, etc.
The implementation of standards and standard configuration:
GB/T4689.20-1996 Measuring fastness of leather’s adhesion
QB/T2710-2005 Measuring leather’s expansion and the rate of elongation
QB/T2711-2005 measuring tear force of leather
QB/T2712-2005 measuring leather’s strength and stretch of spherical crack test
2. VEW 2308A

The machine is designed by mechanical-electrical integration, the composition of the force-measuring Sensor, transmitter, microprocessor, mechanism of load drive, computer and color inkjet printer. The high-precision electronic motor can be set to five-speed, the components are connected by plug-way, Floor-standing models, it is taken account of modern industrial design and ergonomics in modelling and Coating.
It can be tested with all the materials in a stretch, compression, bending, shear, embedded relay, Peeling. tearing, crack, etc, such as rubber, plastics, leather, metal, nylon wire, fabric, paper, aerospace, packaging, construction, petrochemical, electrical, vehicle, etc.
The implementation of standards and standard configuration:
- GB/T4689.20-1996 Measuring fastness of leather’s adhesion
- QB/T2710-2005 Measuring leather’s expansion and the rate of elongation
- QB/T2711-2005 measuring tear force of leather
- QB/T2712-2005 measuring leather’s strength and stretch of spherical crack test
- Test procedure
To run the test, begin by die cutting, sawing, or injection molding your samples to a shape specified in the ASTM specification.
- Prepare specimens and measure the width and the thickness at mid-length.
- Adjust the support span length that you find in the standard determined by your sample size.
- Place the test bar on the 3 point bend fixture and begin the test at the rate specified rates in the standard.
- Record the force and the corresponding deflection.
Measurements
- Flexural Stress
- Flexural Strain
- Flexural Modulus
